name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse <div class="my-header"><span> <a href="/training-material/topics/dev" title="Return to topic page" ><i class="fa fa-level-up" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> <a href="https://github.com/galaxyproject/training-material/edit/main/topics/dev/tutorials/interactive-environments/slides.html"><i class="fa fa-pencil" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> </span></div> <div class="my-footer"><span> <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTN-60px.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" style="height: 40px;"/> </span></div> --- <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTNLogo1000.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" class="cover-logo"/> <br/> <br/> # Galaxy Interactive Environments <br/> <br/> <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> <ul class="text-list"> <li> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/shiltemann/" class="contributor-badge contributor-shiltemann"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/shiltemann?s=36" alt="Saskia Hiltemann avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Saskia Hiltemann</a> <li> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/bgruening/" class="contributor-badge contributor-bgruening"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/bgruening?s=36" alt="Björn Grüning avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Björn Grüning</a> <li> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/hexylena/" class="contributor-badge contributor-hexylena"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/hexylena?s=36" alt="Helena Rasche avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Helena Rasche</a></li> </ul> </div> </div> <!-- modified date --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 8em;"> <i class="far fa-calendar" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">last_modification</span> Updated: <i class="fas fa-fingerprint" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">purl</span><abbr title="Persistent URL">PURL</abbr>: <a href="https://gxy.io/GTN:S00048">gxy.io/GTN:S00048</a> </div> <!-- other slide formats (video and plain-text) --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 5em;"> <i class="fas fa-file-alt" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">text-document</span><a href="slides-plain.html"> Plain-text slides</a> | </div> <!-- usage tips --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 2em;"> <strong>Tip: </strong>press <kbd>P</kbd> to view the presenter notes | <i class="fa fa-arrows" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">arrow-keys</span> Use arrow keys to move between slides </div> ??? Presenter notes contain extra information which might be useful if you intend to use these slides for teaching. Press `P` again to switch presenter notes off Press `C` to create a new window where the same presentation will be displayed. This window is linked to the main window. Changing slides on one will cause the slide to change on the other. Useful when presenting. --- ## Requirements Before diving into this slide deck, we recommend you to have a look at: - Docker basics --- ### <i class="far fa-question-circle" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">question</span> Questions - What are Galaxy Interactive Environments (GIEs)? - How to enable GIEs in Galaxy? - How to develop your own GIE? --- ### <i class="fas fa-bullseye" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">objectives</span> Objectives - Implement a Hello-World Galaxy Interactive Environment --- # Interactive Environments --- ### Why IEs? - Embedded access to third-party application inside of Galaxy - Interactively analyze data, access analysis products within Galaxy 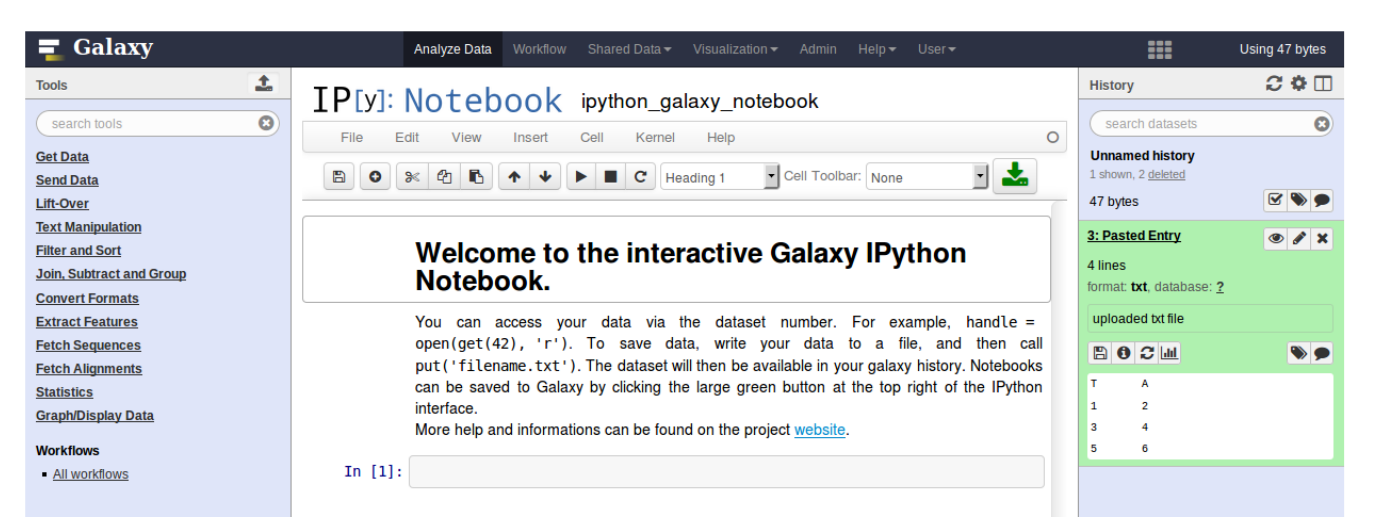 - Bring external analysis platform to the data instead of vice-versa - no need to download/re-upload your data --- ### Who should use IEs? - Everyone! - Programming Environments for Bioinformaticians and Data Scientists - Jupyter - Rstudio - Visualization IEs are great for life scientists - IOBIO (bam/vcf visualizations) - Phinch (metagenomics visualizations) --- ## Types of visualizations in Galaxy GIE for visualization? Check that it is the right choice for your project - **Trackster** - built-in genome browser - **Display applications** - UCSC Genome Browser - IGV - **Galaxy tools** - JBrowse - Krona - **Visualization plugins** - Charts - Generic - **Interactive Environments** - Jupyter/Rstudio - IOBIO (bam/vcf visualizations) - Phinch (metagenomics visualizations) --- ## Which should I use? 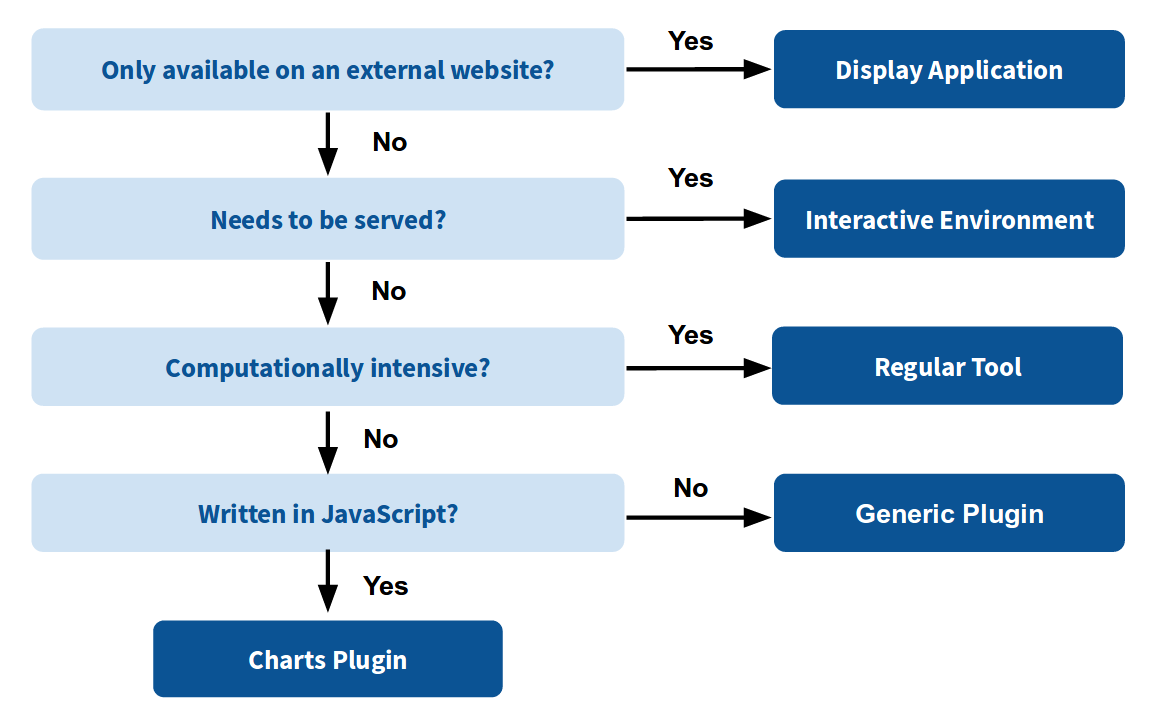 --- ### How to launch an IE? - Can be bound to specific datatypes - Available under the visualizations button on the dataset .image-25[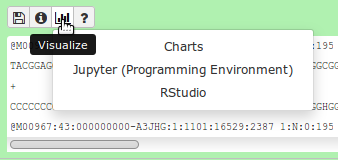] - Or more general-purpose applications (Jupyter/Rstudio) - IE launcher .image-25[] --- ### IE Launcher - Choose between different available docker images - Attach one or more datasets from history .image-75[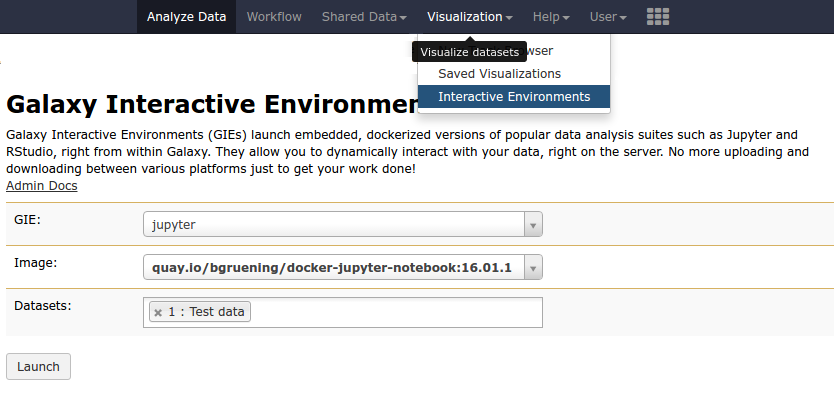] --- ### How does it work? - Docker Containers are launched on-demand by users.. - ..and killed automatically when users stop using them 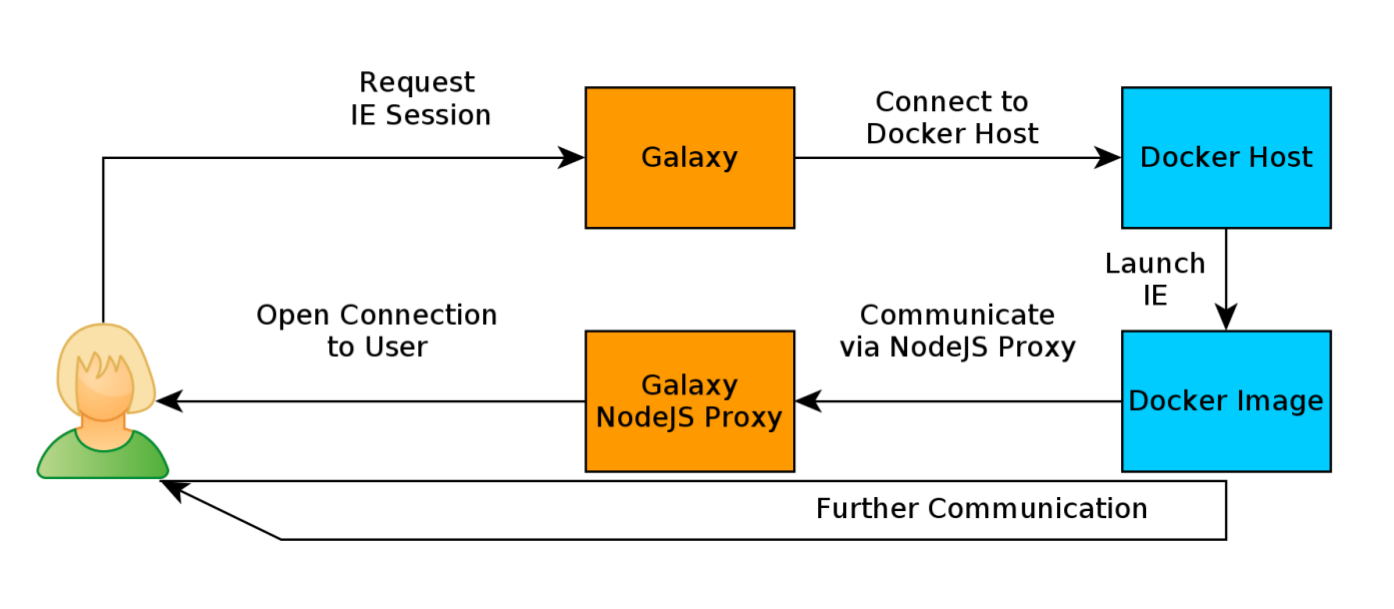 .footnote[ Admin Docs: https://docs.galaxyproject.org/en/master/admin/interactive_environments.html ] --- ### Jupyter - General purpose/ multi-dataset - Provides special functions to interact with the Galaxy history (get/put datasets) - Ability to save and load notebooks .image-75[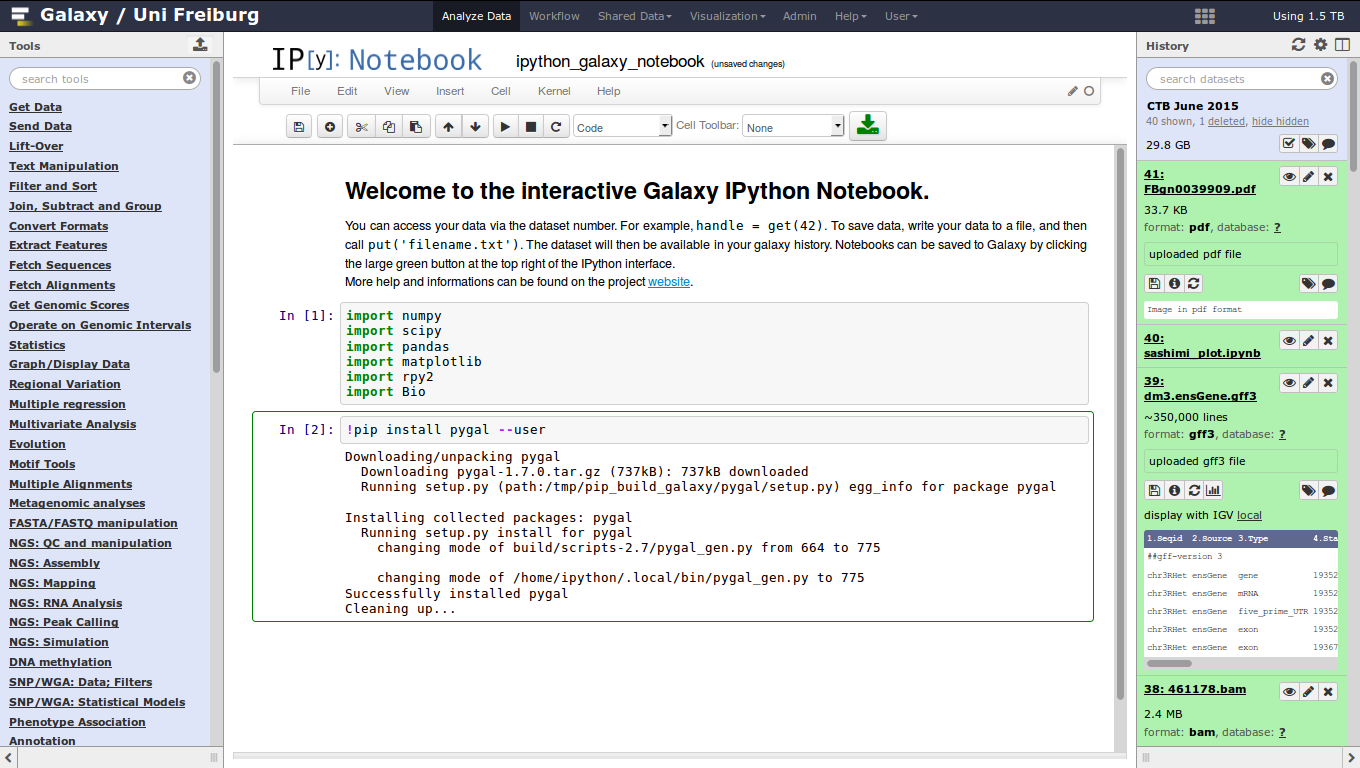] --- ### Jupyter 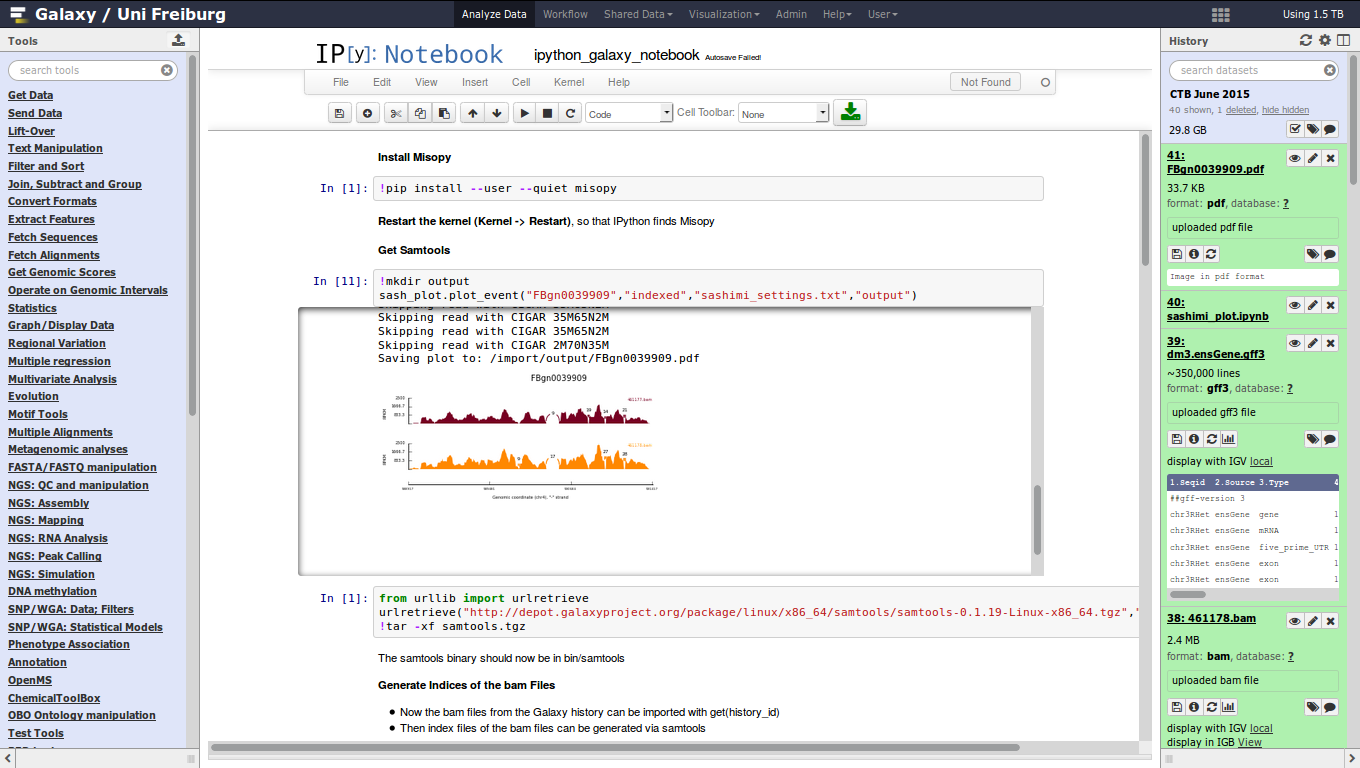 --- ### Jupyter 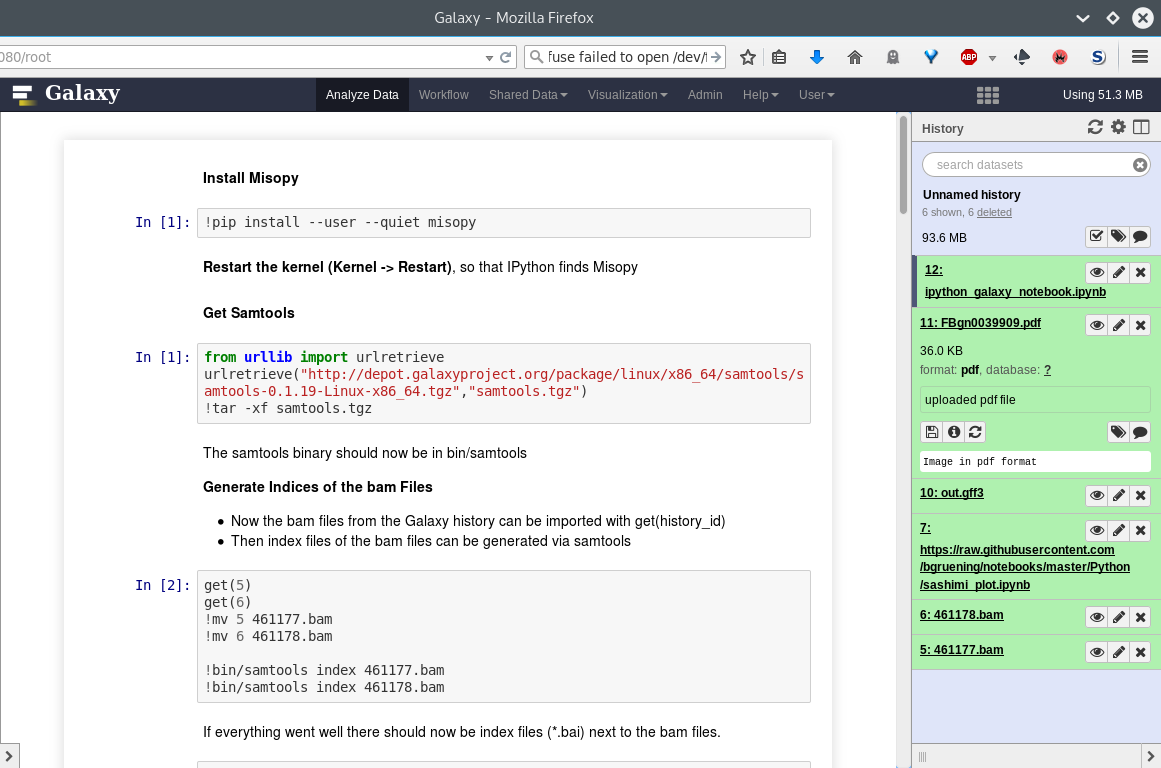 --- ### Rstudio - General purpose/ multi-dataset - Provides special functions to interact with the Galaxy history - Ability to save and load workbook and R history object 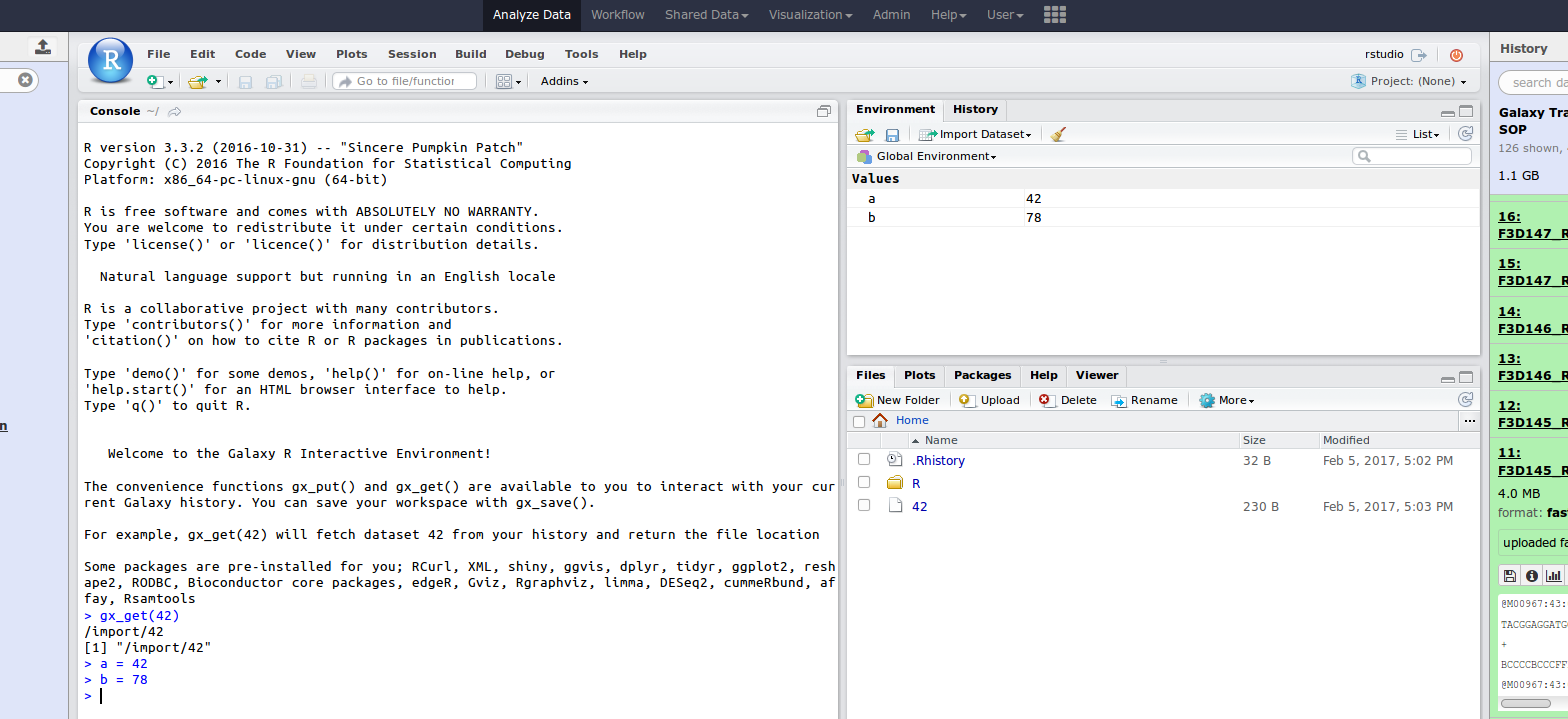 --- ### IOBIO - Visualizes single dataset - Only available for datasets of specific formats 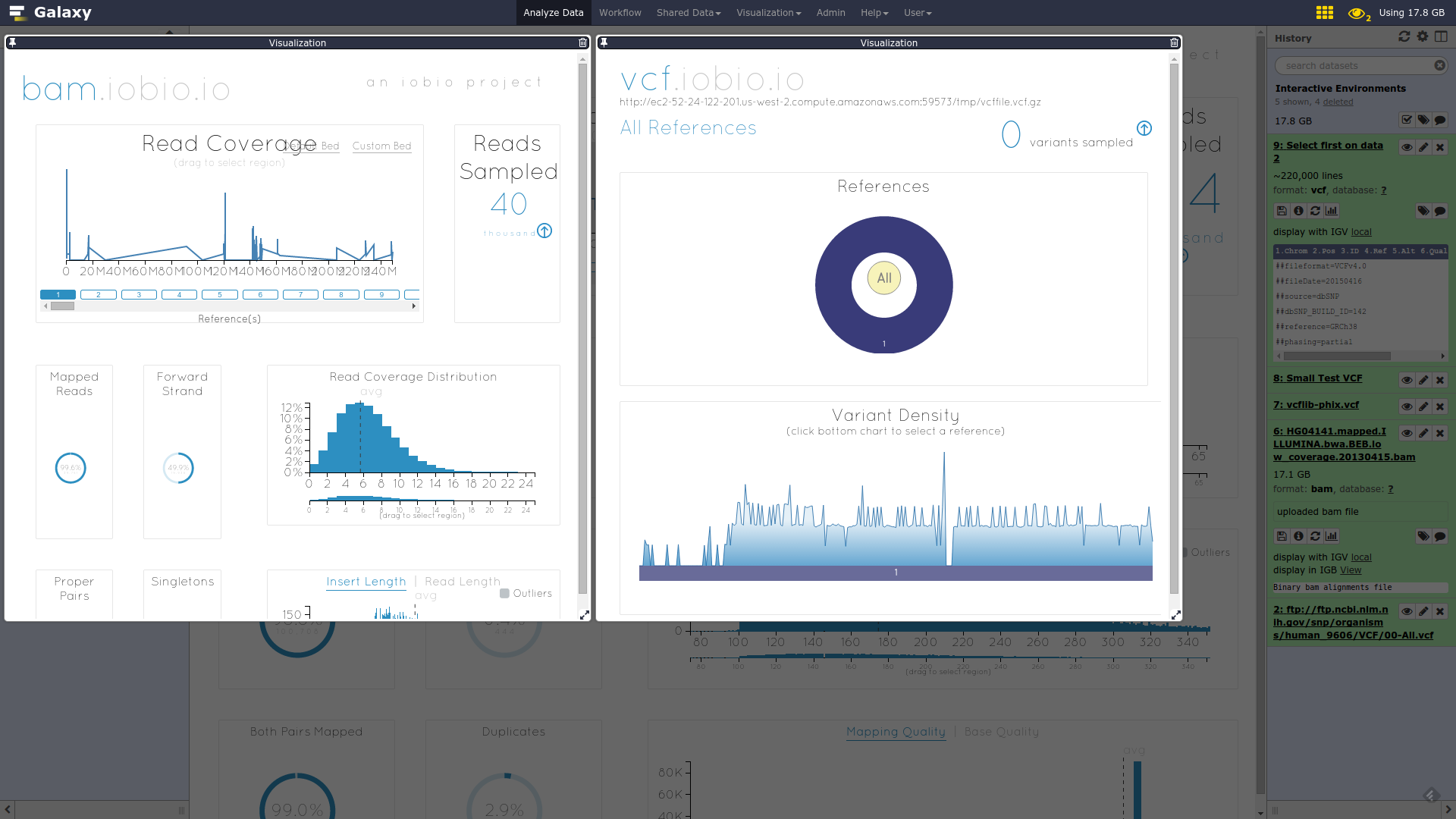 --- ### IOBIO 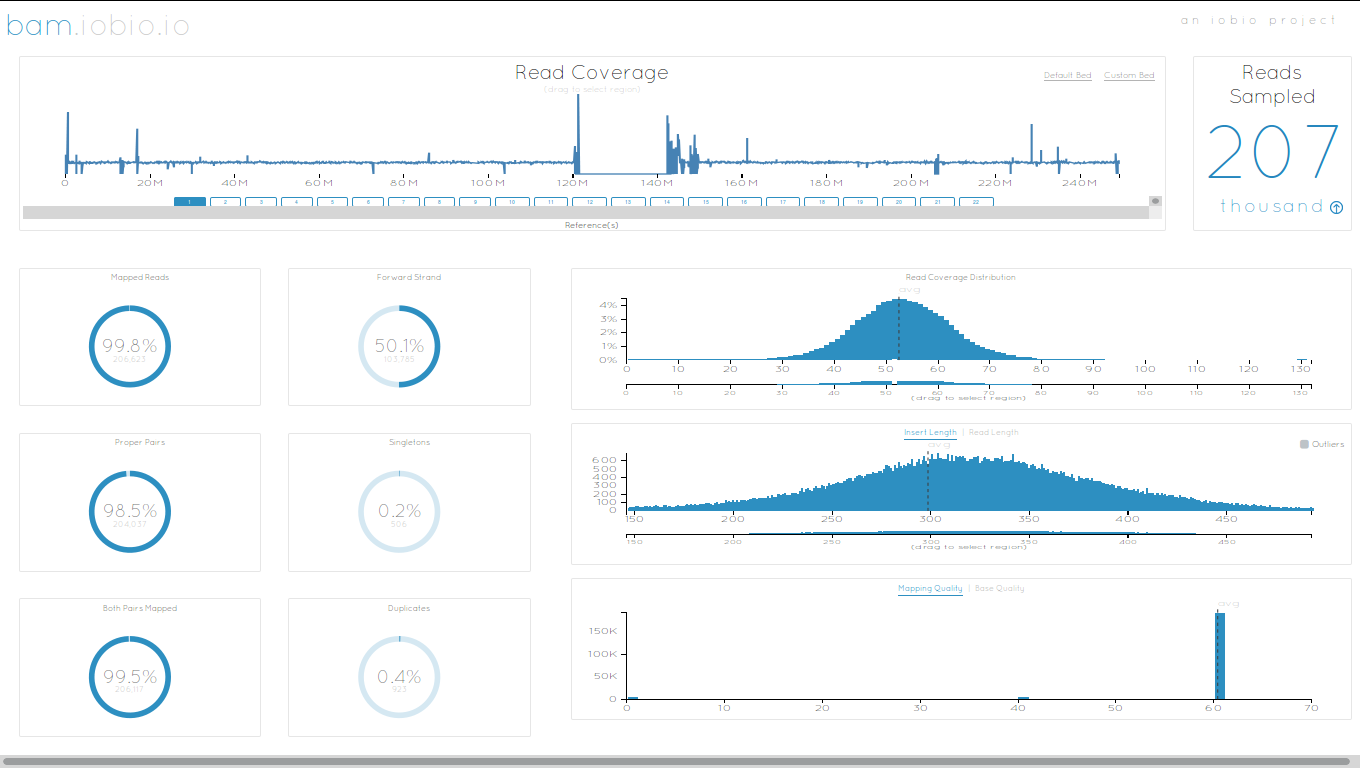 --- ### Phinch 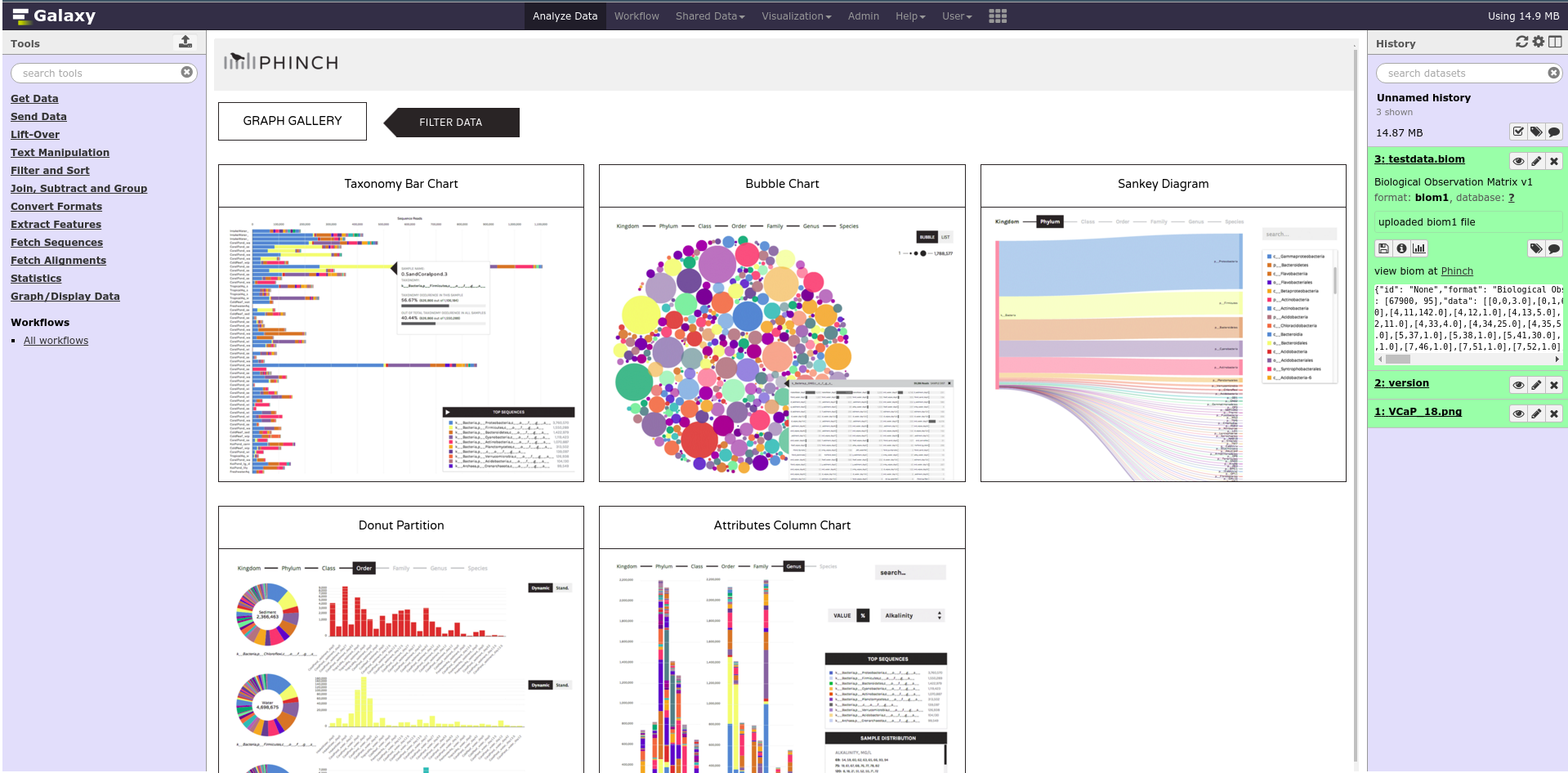 --- ### Admin - Prerequisites: NodeJs (npm) and Docker; Galaxy user must be able to talk to the docker daemon - Enable IEs in `galaxy.yml` ```bash interactive_environment_plugins_directory = config/plugins/interactive_environments ``` - Install node proxy ```bash $ cd $GALAXY/lib/galaxy/web/proxy/js/ $ npm install . ``` - Can configure GIEs to run on another host .footnote[ Advanced configurations: https://docs.galaxyproject.org/en/master/admin/interactive_environments.html] --- ### Development - Not hard to build! - All the magic is in: ```bash $GALAXY/config/plugins/interactive_environments/$ie_name/ ``` | Component | File | |------------------------------------|------------------------------| | Visualization Plugin Configuration | ../config/${ie_name}.xml | | IE specific Configuration | ../config/${ie_name}.ini | | Mako Template | ../templates/${ie_name}.mako | --- ### Development 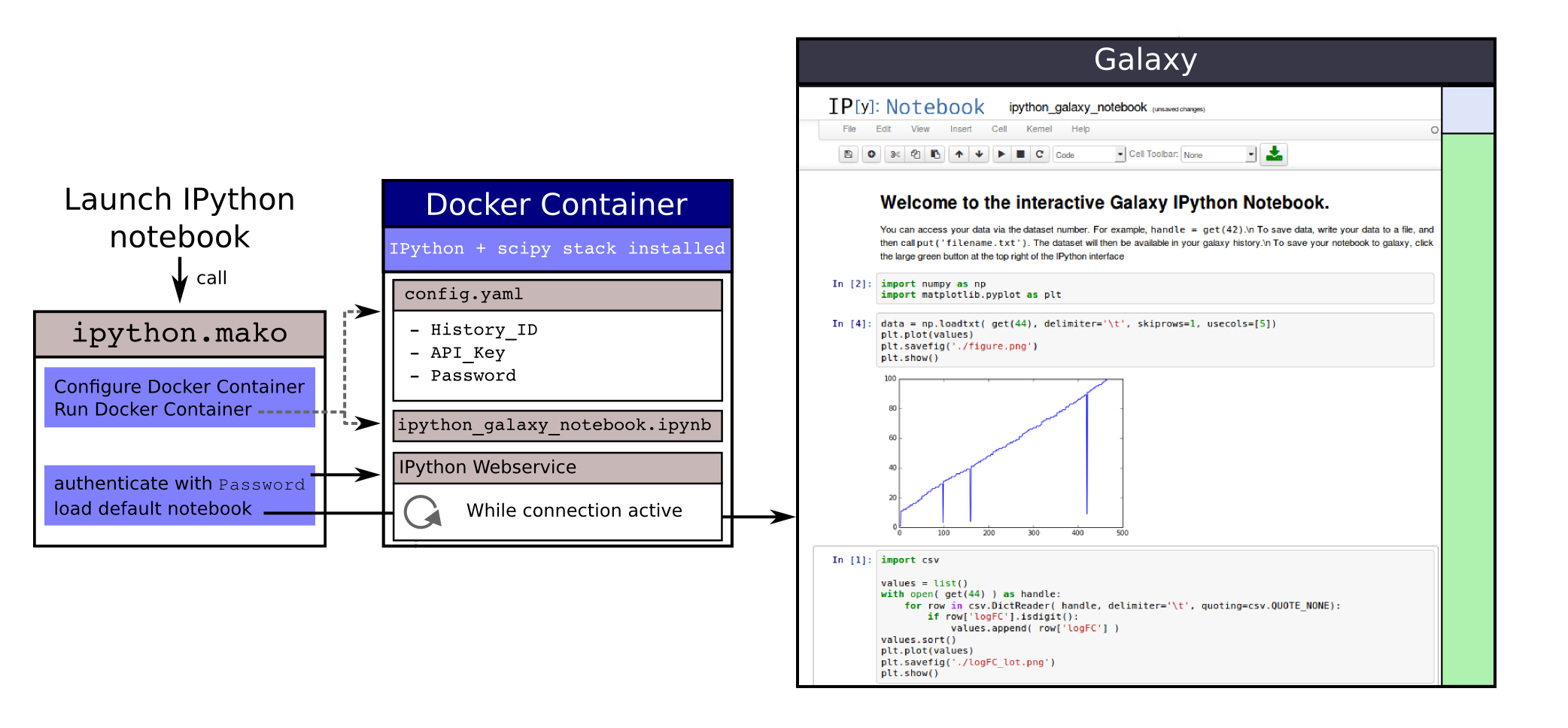 --- ### Hello World Example - All files in this example available from https://github.com/hexylena/hello-world-interactive-environment/ - Create a GIE that shows the directory listing of `import` folder (datasets loaded into GIE by user) ```bash $ tree $GALAXY_ROOT/config/plugins/interactive_environments/helloworld/ config/plugins/interactive_environments/helloworld/ ├── config │ ├── helloworld.ini │ ├── helloworld.ini.sample │ └── helloworld.xml ├── static │ └── js │ └── helloworld.js └── templates └── helloworld.mako ``` --- Create GIE plugin XML file `config/helloworld.xml` ```xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE interactive_environment SYSTEM "../../interactive_environments.dtd"> <!-- This is the name which will show up in the User's Browser --> <interactive_environment name="HelloWorld"> <data_sources> <data_source> <model_class>HistoryDatasetAssociation</model_class> <!-- filter which types of datasets are appropriate for this GIE --> <test type="isinstance" test_attr="datatype" result_type="datatype">tabular.Tabular</test> <test type="isinstance" test_attr="datatype" result_type="datatype">data.Text</test> <to_param param_attr="id">dataset_id</to_param> </data_source> </data_sources> <params> <param type="dataset" var_name_in_template="hda" required="true">dataset_id</param> </params> <!-- Be sure that your entrypoint name is correct! --> <entry_point entry_point_type="mako">helloworld.mako</entry_point> </interactive_environment> ``` --- Set up `.ini` file, which controls docker interaction `config/helloworld.ini.sample` ```ini [main] # Unused [docker] # Command to execute docker. For example `sudo docker` or `docker-lxc`. #command = docker {docker_args} # The docker image name that should be started. image = hello-ie # Additional arguments that are passed to the `docker run` command. #command_inject = --sig-proxy=true -e DEBUG=false # URL to access the Galaxy API with from the spawn Docker container, if empty # this falls back to galaxy.yml's galaxy_infrastructure_url and finally to the # Docker host of the spawned container if that is also not set. #galaxy_url = # The Docker hostname. It can be useful to run the Docker daemon on a different # host than Galaxy. #docker_hostname = localhost [..] ``` --- - Create mako template `templates/helloworld.mako` - Loads configuration from `ini` file - launches docker container, - builds a URL to the correct endpoint through Galaxy NodeJS proxy - set environment variable `CUSTOM` to be passed to container - attach dataset selected by user (`hda`) ```mako <%namespace name="ie" file="ie.mako" /> <% # Sets ID and sets up a lot of other variables ie_request.load_deploy_config() # Define a volume that will be mounted into the container. # This is a useful way to provide access to large files in the container, # if the user knows ahead of time that they will need it. user_file = ie_request.volume( hda.file_name, '/import/file.dat', how='ro') # Launch the IE. This builds and runs the docker command in the background. ie_request.launch( volumes=[user_file], env_override={ 'custom': '42' } ) [..] ``` --- (continued) ```mako [..] # Only once the container is launched can we template our URLs. The ie_request # doesn't have all of the information needed until the container is running. url = ie_request.url_template('${PROXY_URL}/helloworld/') %> <html> <head> ${ ie.load_default_js() } </head> <body> <script type="text/javascript"> ${ ie.default_javascript_variables() } var url = '${ url }'; ${ ie.plugin_require_config() } requirejs(['interactive_environments', 'plugin/helloworld'], function(){ load_notebook(url); }); </script> <div id="main" width="100%" height="100%"> </div> </body> </html> ``` --- Lastly we must write the `load_notebook` function, `static/js/helloworld.js` ```javascript function load_notebook(url){ $( document ).ready(function() { test_ie_availability(url, function(){ append_notebook(url) }); }); } ``` --- ### Hello World Example - The only thing missing now is the GIE (Docker) container itself - Container typically consists of: - Dockerfile - Proxy configuration (e.g. nginx) - Custom startup script/entrypoint - Script to monitor traffic and kill unused containers - The actual application for the users (here: simple python process which serves directory contents of `/import` folder of container) --- ```dockerfile FROM ubuntu:14.04 # These environment variables are passed from Galaxy to the container # and help you enable connectivity to Galaxy from within the container. # This means your user can import/export data from/to Galaxy. ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive \ API_KEY=none \ DEBUG=false \ PROXY_PREFIX=none \ GALAXY_URL=none \ GALAXY_WEB_PORT=10000 \ HISTORY_ID=none \ REMOTE_HOST=none RUN apt-get -qq update && \ apt-get install --no-install-recommends -y \ wget procps nginx python python-pip net-tools nginx # Our very important scripts. Make sure you've run `chmod +x startup.sh # monitor_traffic.sh` outside of the container! ADD ./startup.sh /startup.sh ADD ./monitor_traffic.sh /monitor_traffic.sh # /import will be the universal mount-point for IPython # The Galaxy instance can copy in data that needs to be present to the # container RUN mkdir /import [..] ``` --- (continued) ```dockerfile [..] # Nginx configuration COPY ./proxy.conf /proxy.conf VOLUME ["/import"] WORKDIR /import/ # EXTREMELY IMPORTANT! You must expose a SINGLE port on your container. EXPOSE 80 CMD /startup.sh ``` --- - Proxy configuration (nginx) - reverse proxy our directory listing process running on port 8000 ```nginx server { listen 80; server_name localhost; # Note the trailing slash used everywhere! location PROXY_PREFIX/helloworld/ { proxy_buffering off; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000/; proxy_redirect http://127.0.0.1:8000/ PROXY_PREFIX/helloworld/; } } ``` --- - Create the `startup.sh` file which starts our directory listing service ```bash #!/bin/bash # First, replace the PROXY_PREFIX value in /proxy.conf with the value from # the environment variable. sed -i "s|PROXY_PREFIX|${PROXY_PREFIX}|" /proxy.conf; # Then copy into the default location for ubuntu+nginx cp /proxy.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default; # Here you would normally start whatever service you want to start. In our # example we start a simple directory listing service on port 8000 cd /import/ && python -mSimpleHTTPServer & # Launch traffic monitor which will automatically kill the container if # traffic stops /monitor_traffic.sh & # And finally launch nginx in foreground mode. This will make debugging # easier as logs will be available from `docker logs ...` nginx -g 'daemon off;' ``` --- - Lastly, the script to monitor traffic and shut down if user is no longer connected, `monitor_traffic.sh` ```bash #!/bin/bash while true; do sleep 60 if [ `netstat -t | grep -v CLOSE_WAIT | grep ':80' | wc -l` -lt 3 ] then pkill nginx fi done ``` --- ### Hello World Example - We are now ready to build our container, and try out our new GIE! - If the container is hosted on a service like Dockerhub or quay.io, it will be automatically fetched on first run. ```bash $ cd hello-ie $ docker build -t hello-ie . ``` 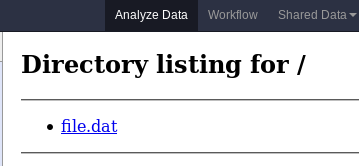 .footnote[Try it yourself: https://github.com/hexylena/hello-world-interactive-environment] --- ### <i class="fas fa-key" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">keypoints</span> Key points - Interactive Environments offer access to third-party applications within Galaxy - Interactive Environments run in a docker images for sandboxing and easy dependency management --- ## Thank You! This material is the result of a collaborative work. Thanks to the [Galaxy Training Network](https://training.galaxyproject.org) and all the contributors! <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> <table class="contributions"> <tr> <td><abbr title="These people wrote the bulk of the tutorial, they may have done the analysis, built the workflow, and wrote the text themselves.">Author(s)</abbr></td> <td> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/shiltemann/" class="contributor-badge contributor-shiltemann"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/shiltemann?s=36" alt="Saskia Hiltemann avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Saskia Hiltemann</a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/bgruening/" class="contributor-badge contributor-bgruening"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/bgruening?s=36" alt="Björn Grüning avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Björn Grüning</a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/hexylena/" class="contributor-badge contributor-hexylena"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/hexylena?s=36" alt="Helena Rasche avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Helena Rasche</a> </td> </tr> <tr class="reviewers"> <td><abbr title="These people reviewed this material for accuracy and correctness">Reviewers</abbr></td> <td> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/shiltemann/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-shiltemann"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/shiltemann?s=36" alt="Saskia Hiltemann avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/bgruening/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-bgruening"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/bgruening?s=36" alt="Björn Grüning avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/nsoranzo/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-nsoranzo"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/nsoranzo?s=36" alt="Nicola Soranzo avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/hexylena/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-hexylena"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/hexylena?s=36" alt="Helena Rasche avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/martenson/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-martenson"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/martenson?s=36" alt="Martin Čech avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/bebatut/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-bebatut"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/bebatut?s=36" alt="Bérénice Batut avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/lecorguille/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-lecorguille"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/lecorguille?s=36" alt="Gildas Le Corguillé avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/gallardoalba/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-gallardoalba"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/gallardoalba?s=36" alt="Cristóbal Gallardo avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/njall/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-njall"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/njall?s=36" alt="Niall Beard avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a></td> </tr> </table> </div> </div> <div style="display: flex;flex-direction: row;align-items: center;justify-content: center;"> <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTNLogo1000.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" style="height: 100px;"/> </div> Tutorial Content is licensed under <a rel="license" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/">Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License</a>.<br/>